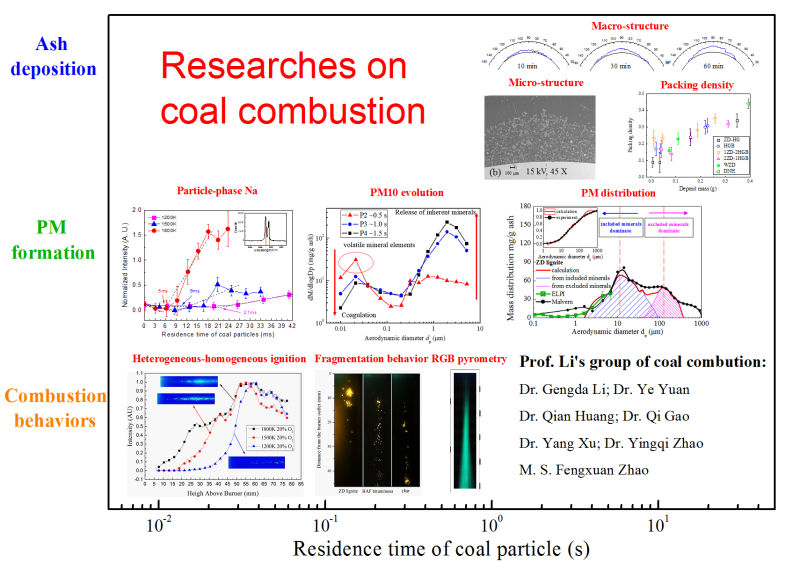
This figure illustrates our fundimental researches on coal combustion, as a function of coal particle residence time in high-temperature ambiences. Combined with advanced in-situ diagnostics as well as standard off-line measurements, aspects like particle ignition, surface temperature, fragmentation properties, minerals relea...
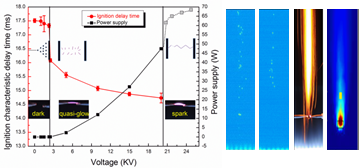
The plasma-assisted ignition enhancement of pulverized lignite particles is intensively studied in a laminar, upward Hencken flat-flame burner. Under the conditions of different oxygen mole fractions, the discharge mechanisms and the reductions of ignition delay time are examined to distinguish the chemical and thermal effect...
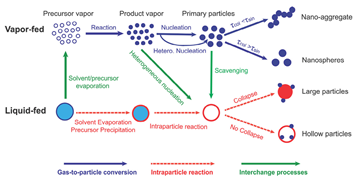
Manufacturing of nanostructured materials and functional devices offers many exciting opportunities for substantial contribution in renewable energy utilization, environmental compliance, and product development. In the past two decades, gas-phase flame synthesis has not only proved to be one of the most scalable and economic...
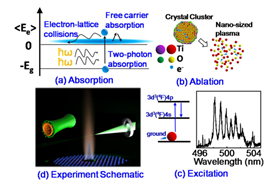
The absorption-ablation-excitation mechanism in laser-cluster interactions is investigated by measuring Rayleigh scattering of aerosol clusters along with atomic emission from phase-selective laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. For 532 nm excitation, as the laser intensity increases beyond 0.16 GW/cm2, the scatte...
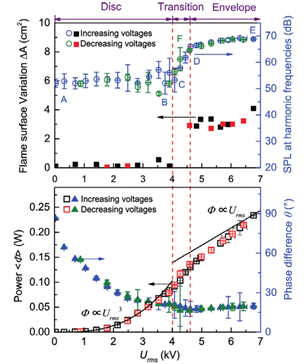
We present a novel phenomenon of low-frequency AC electric field induced thermoacoustic oscillations by employing a wall-jet premixed stagnation flame configuration. A high speed camera and a microphone are used to record the instantaneous flame topographies and the acoustic oscillations, respectively. We find that, under man...
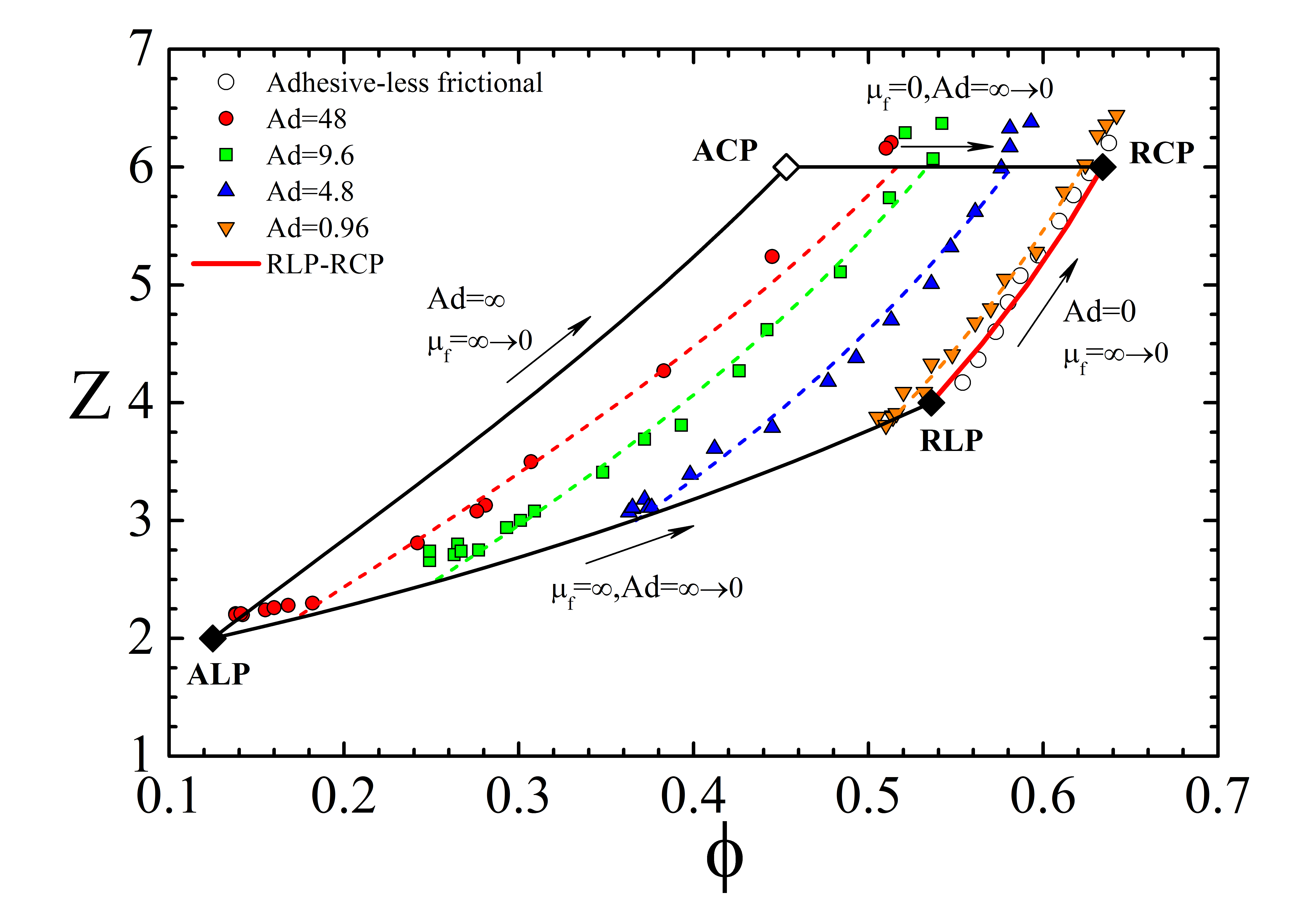
The packings of non-adhesive granular matter have been extensively studied, with two well-known packing limits identified as the Random Close Packing (RCP) and the Random Loose Packing (RLP). However, for micron-sized particles, the presence of adhesive interactions such as van der Waals forces could intrinsically change ...
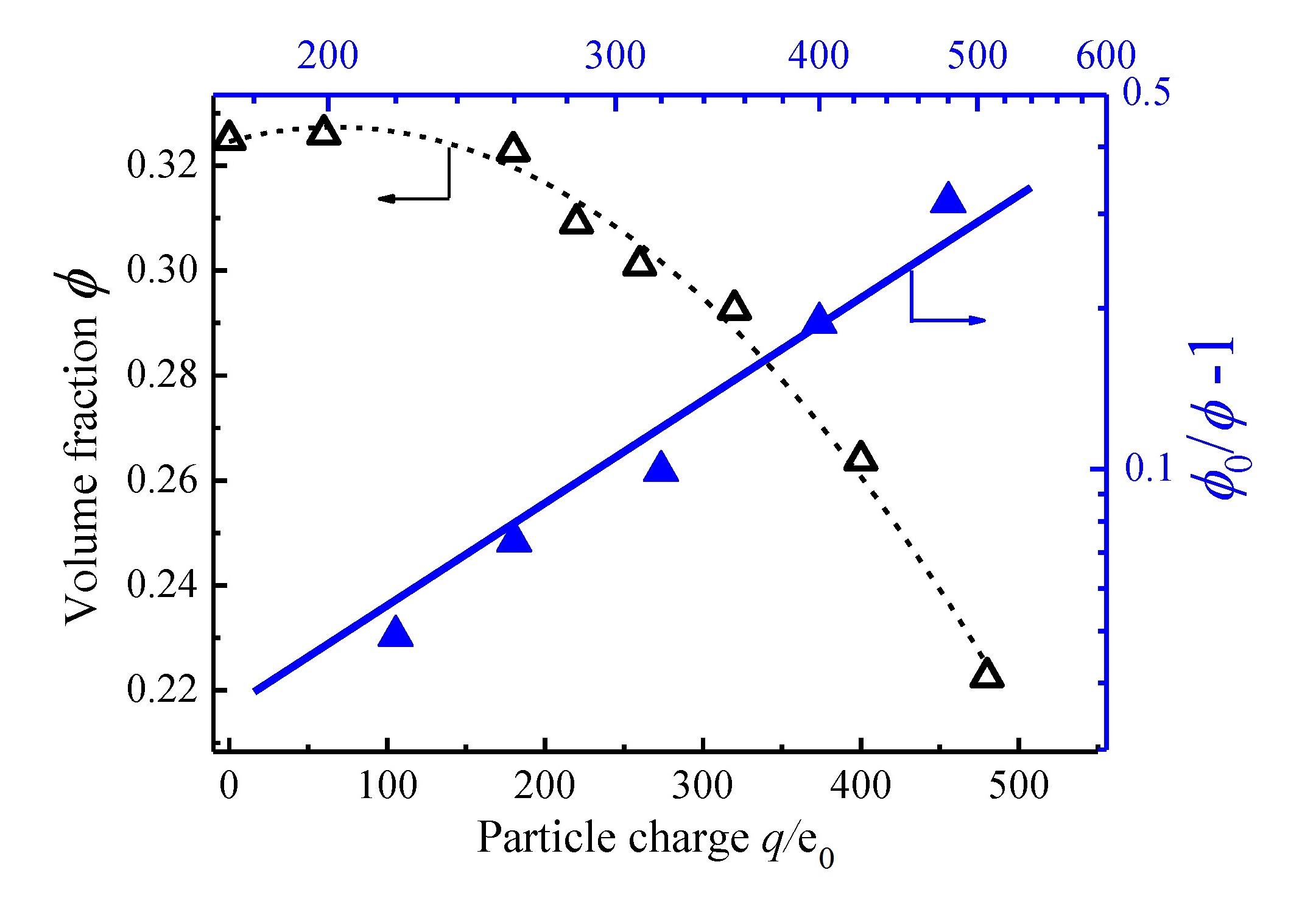
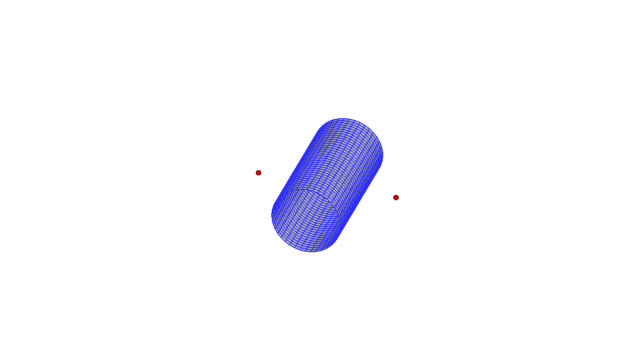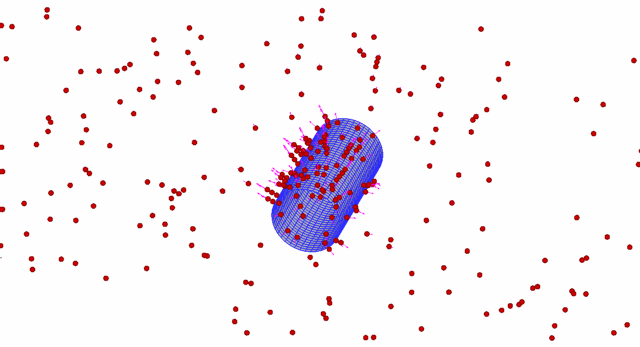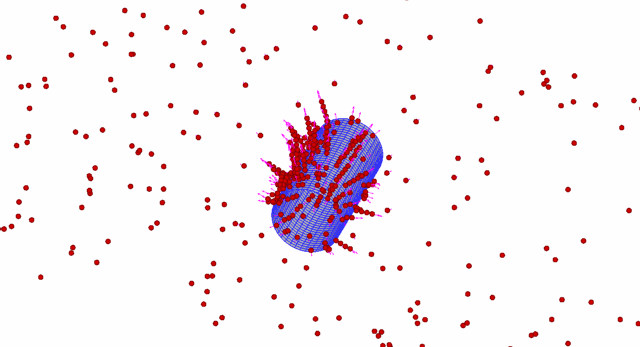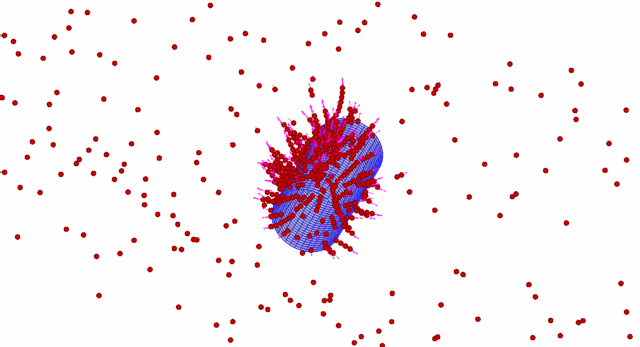
Different from the short-range van der Waals interactions, the electrostatic forces can exert their influence across a much longer distance, which cause profound changes in the structure of a particulate system and offer the ability to manipulate particles at the microscales. One of these electrokinetic phenomena related ...
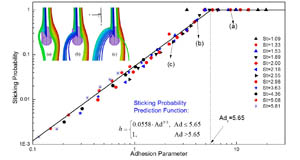
The impaction-sticking mechanism of fine particulates plays a significant role in a wide range of applications from dust separation device, thin-film deposition technique to astrophysics science, but the underlying physics is less clarified. In this paper, a discrete element (DEM) method approach is established to investigate...
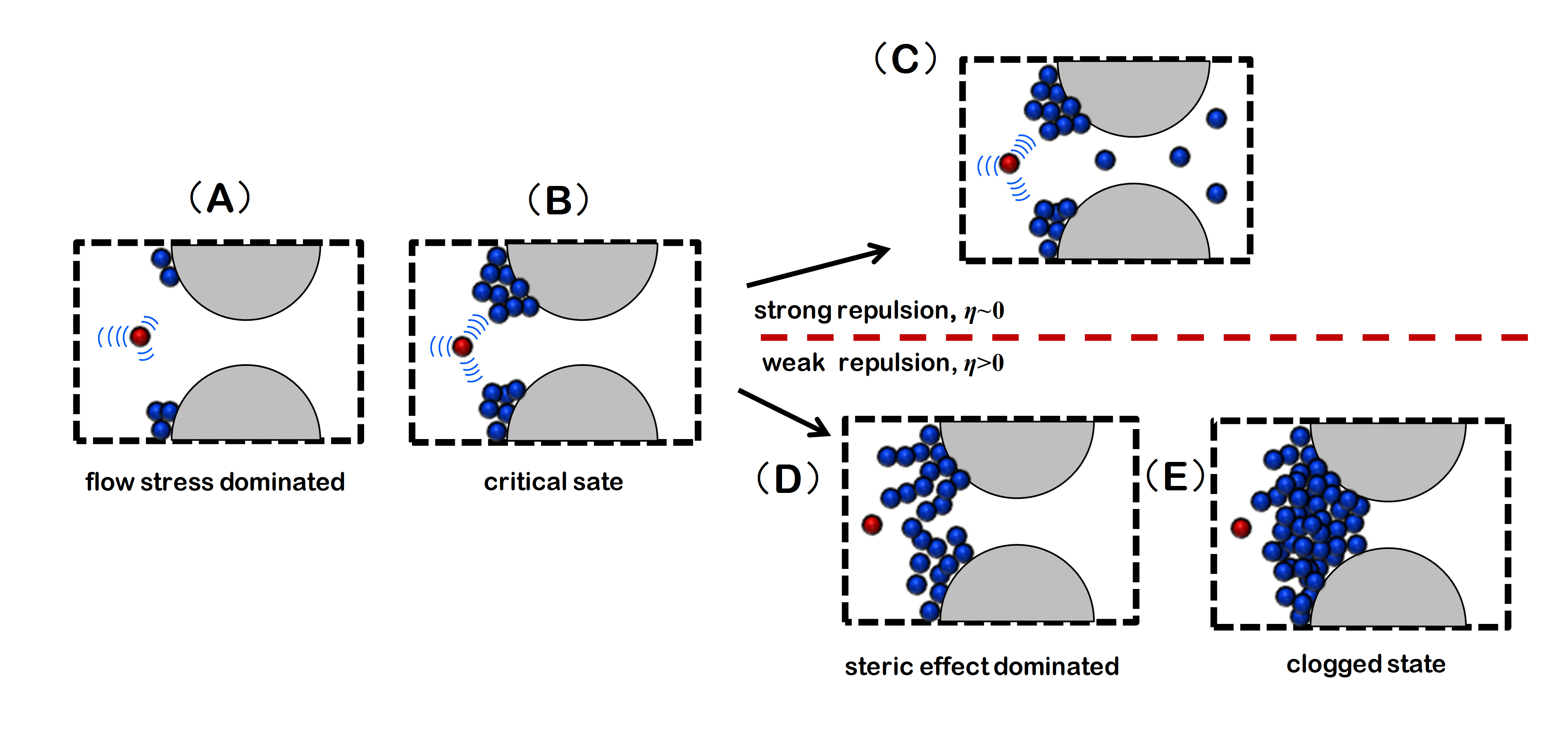
Pore clogging caused by microscale particles exists universally in various engineering processes, including transport of biological cells, aerosol filtration, assay applications of colloidal particles, and microreactors. We perform computer simulations based on adhesive contact mechanics to demonstrate the clogging process of...
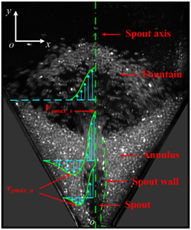
Two-dimensional spouted bed, capable to provide both dilute granular gas and dense granular solid flow patterns in one system, was selected as a prototypical system for studying granular materials. Effects of liquid cohesion on such kind of complex granular patterns were studies for the first time, using particle image veloci...
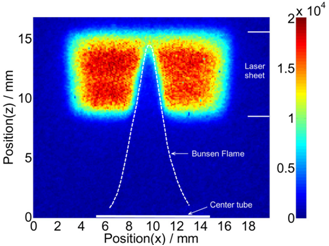
Two-dimensional imaging of gas/particle phase transition of metal oxides in their native high-temperature flow conditions, using laser-driven localized nanoplasmas, was obtained by utilizing the gap between the excitation energies of the gas and particle phases such that only the Ti atoms in the particle phase were selectively...
A discrete-element method is developed for applications involving interaction of spherical particles with a body of arbitrary shape in an electrostatic field. The electric field is induced both by charged particles and by other ‘macroscopic’ bodies (e.g. electrodes). The electric field due to macroscopic bodies is co...