- coal combustion Position :Home -- Research -- coal combustion
-
Particulate Formation and Ash Deposition of Oxy-Coal Combustion
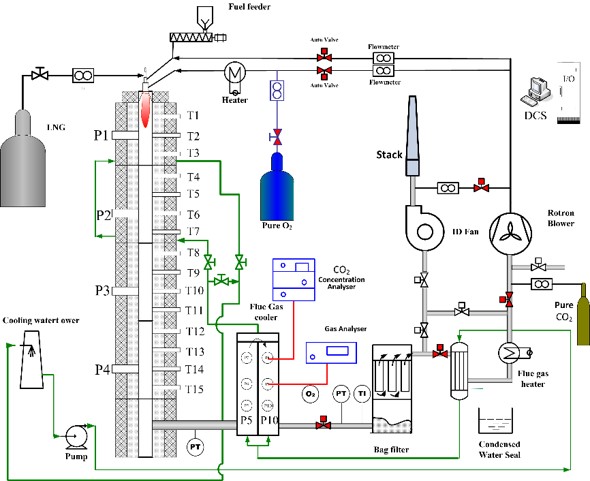
The characteristics of both particulate formation and ash deposition play an important role in retrofitting the conventional air-fired coal power plant into the recycled oxy-fuel plant. An intensively comparative study was performed with a 25 kW quasi one-dimensional down-fired pulverized coal combustor for clarifying the differences between air combustion and recycled oxy-fuel combustion of bituminous coal. In oxy-fuel mode, the oxygen concentration was set at 30% to provide a similar heat flux output to the air mode. The results indicated that, under similar furnace temperature profiles, the oxy-fuel combustion leads to the higher fine particulate formation, finer bulk ash particle formation and lower ash deposition. The aerodynamic factor, instead of the chemical composition related to fine particulates, determines the difference in the ash deposition behavior in two combustion model.
Publication: Li GD, Li S, Dong M, Yao Q, Guo CY, Axelbaum RL. Comparison of particulate formation and ash deposition under oxy-fuel and conventional pulverized coal combustions. Fuel, 106: 544-551 (2013).
Prev:Dynamic Behavior of Biomass Ash Deposition[ Return ]
Next:Combustion behaviors, PM formation, and ash deposition during coal combustion